A Switching Power Supply is essential in modern electronics. It converts electrical energy efficiently with minimal heat. This technology is widely used in computers, televisions, and various appliances. Unlike traditional power supplies, it switches components on and off to regulate voltage.
Understanding how a Switching Power Supply operates is crucial. It relies on high-frequency switching to minimize energy loss. This results in a lighter, more compact design compared to linear power supplies. However, it can create unwanted electromagnetic interference. Designers must address this issue to ensure reliable operation.
Many people underestimate the complexity of this technology. A simple issue can lead to performance problems. Engineers must carefully consider every component. Despite its advantages, some may find it challenging. It is a field that requires continuous learning and improvement.
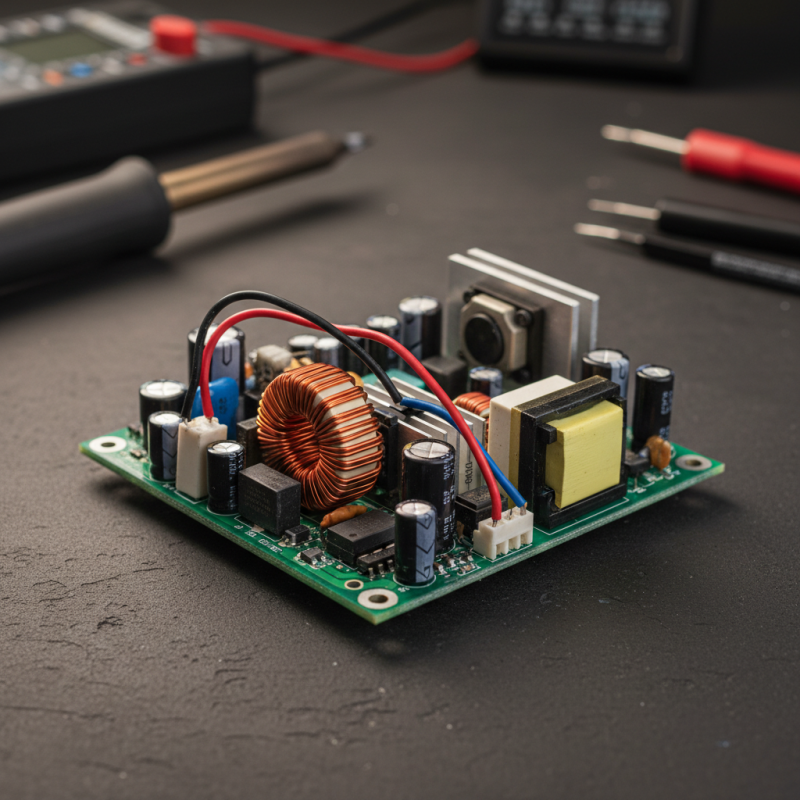
A switching power supply is a crucial component in many electronic devices. Its primary function is to convert electrical power efficiently. Unlike traditional power supplies, switching power supplies use a high-frequency switching mechanism. This involves rapidly turning the power flow on and off, allowing for more efficient energy conversion.
One key aspect of a switching power supply is its ability to regulate voltage levels. This regulation is vital for protecting sensitive electronic components. By maintaining a steady output voltage, switching power supplies enhance device reliability. However, the design can be complex, leading to challenges in thermal management and electromagnetic interference. Sometimes, these issues might disrupt the overall efficiency we seek.
When using a switching power supply, it's important to consider its efficiency. Many users overlook the importance of proper circuit design. Poor layout can lead to unintended signal noise. This can affect performance and longevity. Understanding these nuances is essential for optimizing power supply functionality. Balancing efficiency and complexity often requires careful planning and testing.
A switching power supply (SPS) operates by converting electrical energy efficiently. Its core components play crucial roles. The input stage receives AC voltage, transforming it into DC voltage. This stage is vital for the entire process.
The heart of the SPS is the switching element. It rapidly turns on and off, controlling the output voltage. This component allows for compact designs. However, poor quality can lead to inefficient energy use. Alongside it, the transformer boosts or reduces voltage levels. The magnetic core can become hot if not designed well, impacting performance.
Filters and control circuits work together to maintain stability. Filters smooth out voltage fluctuations. Control circuits manage the switching speed, ensuring consistency. A poorly calibrated control circuit may result in unwanted noise or voltage spikes. Each element contributes to efficiency. Yet, the balance between performance and heat generation can be a constant challenge.
Switching power supplies play a critical role in converting input voltage to desired output voltage. They utilize a high-frequency switching technique rather than linear regulation. This method allows for increased efficiency, often exceeding 80%. In contrast, linear power supplies waste energy as heat, primarily using resistive components.
These devices function by rapidly turning the input voltage on and off. This action creates pulses that are easier to transform with inductors and capacitors. The switching frequency typically ranges from 20 kHz to 500 kHz. Higher frequencies can lead to smaller components, which is essential for compact designs. According to a recent industry report, around 60% of all power supplies sold today are switching types, underscoring the widespread adoption.
However, switching power supplies can introduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Designing effective EMI filters becomes a necessity. Failure to address this can lead to non-compliance with regulatory standards. Inherent challenges, like voltage spikes during switching transitions, require careful engineering. Despite these imperfections, advancements continue to enhance their performance and reliability, minimizing such issues over time.
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency of switching power supplies operating at different output voltages. As shown, the efficiency increases with higher output voltages, with the 24V output achieving the highest efficiency rate of 92%.
Switching power supplies (SMPS) have revolutionized the power electronics landscape. One major advantage is their efficiency. Research shows they can achieve efficiency ratings above 90%. In contrast, linear regulators often operate at lower efficiency, particularly under varying loads. This disparity can lead to significant energy loss in linear power supplies, especially in high-output applications.
SMPS are compact. They can deliver higher power output within smaller form factors. This is crucial in modern electronics where space is at a premium. In a typical linear regulator setup, heat dissipation becomes a concern. A considerable amount of energy is lost as heat, increasing thermal management challenges. Data suggests that well-designed SMPS can handle significant loads without excessive heat generation.
However, not everything is perfect with SMPS. The complexity of their design may pose challenges for certain applications. Some users may face electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues. Moreover, switching noise can affect sensitive devices. Balancing these factors requires careful engineering choices. Industry reports indicate that while SMPS are becoming the standard, understanding their limitations is essential for effective application.
Switching power supplies are crucial in modern electronics. They efficiently convert electrical power from one voltage level to another. You can find them in various devices, from laptops to smartphones. Their compact size and light weight make them ideal for portable gadgets.
In industrial applications, switching power supplies are often used for automation systems. They power sensors and actuators reliably. Additionally, they support renewable energy systems, like solar panels. However, designing a switching power supply can be complex. Engineers must consider efficiency, heat dissipation, and electromagnetic interference. These factors can complicate the design process.
In consumer electronics, switching power supplies are vital for chargers. They allow devices to run with minimal energy loss. Despite their benefits, they can generate noise. This can affect nearby sensitive components. Balancing performance and noise is an ongoing challenge for designers.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | Typically 100-240V AC or 12-48V DC |
| Output Voltage | Varies depending on design, can be 5V, 12V, 24V, etc. |
| Efficiency | Typically 70% to 90% depending on design |
| Common Applications | Computers, telecommunication equipment, consumer electronics |
| Control Methods | Voltage mode, current mode, frequency modulation |
| Key Components | Transistors, inductors, capacitors, diodes |
| Output Ripple | Low, due to filtering components |
| Size and Weight | Compact design, lightweight compared to linear supplies |
Update your browser to view this website correctly. Update my browser now
